Learn About The Little-Albert Experiment

John B. Watson is known as one of the fathers of behaviorism. His main intellectual inspiration was Ivan Pavlov, the Russian physiologist who made the first discoveries regarding conditioning. Following these discoveries, Watson conducted a famous study called the Little-Albert experiment.
Pavlov was also the man who conducted a very famous experiment on dogs. You could say that this is one of the experiments that made psychology seen as a real science. With this experiment , Pavlov discovered the basic aspects of stimulus response and established the principles of classical conditioning.
Watson tried to mimic Pavlov’s experiment with the dogs through the Little-Albert experiment. In other words, he conducted the same experiment, but with humans. In this particular case , he manipulated a baby to prove his hypothesis.
Pavlov’s experiments
Ivan Pavlov was a great researcher. After delving into various disciplines, he became interested in physiology. A physiological element was exactly what allowed him to discover conditioning from the stimulus-response model.
For example, Pavlov noted that dogs salivate before being fed. In other words, they prepare for the food itself. This means that they respond to a stimulus.
That observation encouraged Pavlov to conduct an experiment. He did this by exposing the dogs to other stimuli before feeding them, as a sort of announcement.

The most famous stimulus was a bell. Pavlov wanted to prove that if dogs heard a bell often enough before being fed, they would salivate at the sound of the bell. They would do this because the bell would act as an announcement that they would be fed.
So by doing this often enough, Pavlov managed to condition the dogs. The sound of the bell was the stimulus, and the dogs’ saliva was the response.
Background information on the Little-Albert experiment
Watson was a radical positivist. He believed that human behavior should be studied solely on the basis of already learned behavior. General, unconscious or instinctive elements were not important according to him. He only wanted to study behavior that he could observe.
Watson was a researcher at John Hopkins University in Baltimore. He began with the idea that human behavior could be largely, if not entirely, explained by a person’s learning history based on his conditioning.
He therefore thought it a good idea to prove that Pavlov’s conclusions could also be applied to humans.
Watson went to an orphanage with his assistant Rosalie Rayner. Then they chose an 8-month-old baby, the son of one of the nurses from the orphanage.
The baby was very neglected and lived in a very cold, harsh environment. Despite all this, however, the baby seemed very calm. The people there said he hardly cried at all.
This was the beginning of the Little-Albert experiment.
A controversial experiment
In the first phase of the Little-Albert experiment , Albert was exposed to various stimuli. The purpose of this was to see which stimuli made him afraid. She discovered that he was only afraid of loud noises. This is something you often see in babies. Other than that, however, Albert didn’t seem to be afraid of things like animals or fire.
Then they consciously aroused fear in him through conditioning. First of all, they held a white rat in front of him. At first little Albert just wanted to play with it. However, when he tried to do this, Watson made a very loud noise that scared Albert.
After repeating this a few times, Albert finally became afraid of the rat. Then the researchers exposed Albert to other animals as well, such as rabbits, dogs and even fur coats. They managed to condition Albert in relation to all these animals. As a result, he had become afraid of each of these animals.
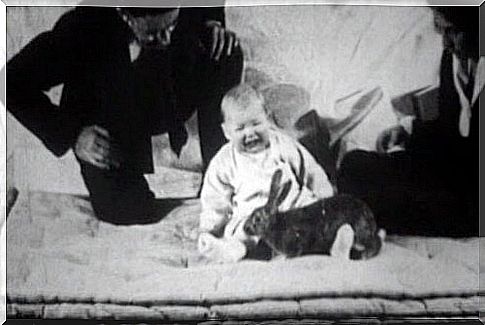
The researchers subjected Albert to these experiments for a very long time. In fact, it went on for almost a year. By the end of the experiment , Albert had gone from a calm baby to an anxious baby.
Even to the point that he got scared at the sight of a mask of Santa Claus. They let him touch the mask, after which he began to cry incessantly.
During the second part of the experiment, Watson wanted to reverse the conditioning. This meant “deconditioning” the fears he had previously conditioned. However, this never happened. The university fired Watson for his controversial experiment and for having started a romance with his assistant.
After the experiment
We don’t know what happened to the baby after the experiment. However, there are articles indicating that the child died at the age of six as a result of congenital hydrocephalus. If true, it means that the results of this cruel experiment are highly questionable.
The Little Albert experiment is one of the best known studies in the history of psychology. Its claims, conclusions and violation of numerous rules made it highly controversial.









